
What is IVF
In vitro traces its origin to Latin and it means ‘in glass’. In medical terms, IVF involves fertilisation or the fusion of the male and female gametes outside of the human body – in a laboratory dish. Due to the nature of the process, the term “test tube baby” is used in common parlance for the procedure.
IVF can be performed in two ways – self cycle and donor cycle. In self cycle, eggs and sperms from the female and male partners, respectively are collected. Donor cycle comprises utilising either egg or sperm or both from a donor; sometimes, even donor embryos may be used in an IVF cycle.
The female egg and the male egg are then fertilised in sterile and controlled laboratory conditions to result in an embryo. The embryo is allowed to develop to the blastocyst stage before it is transferred into the female partner or surrogate’s uterus.
IVF can be performed in two ways – self cycle and donor cycle. In self cycle, eggs and sperms from the female and male partners, respectively are collected. Donor cycle comprises utilising either egg or sperm or both from a donor; sometimes, even donor embryos may be used in an IVF cycle.
The female egg and the male egg are then fertilised in sterile and controlled laboratory conditions to result in an embryo. The embryo is allowed to develop to the blastocyst stage before it is transferred into the female partner or surrogate’s uterus.
Why you need to consult a infertility or IVF Specialist
Tubal blockage
Fallopian tube is the location where fertilisation takes place in the female anatomy. A damage or blockage here would mean that the mature egg isn’t able to follow the course of journey through the fallopian tube and of the fertilised product, embryo, into the uterus.
Ovulation disorders
Disorders related to ovulation would mean the absence of an egg during the fertile period hence, no embryo is formed naturally. This is a reason for infertility.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is the condition in which endometrium – the tissue lining the uterus – grows outside it. This has been found in 10-15% women in the reproductive age and impacts various fertility parameters such as less number of viable eggs (low ovarian reserve), poor quality of eggs and embryo, as well as hindrance to implantation.
Uterine fibroids
These are non-cancerous tumours that grow in the uterus of females in childbearing age. Higher levels of hormones oestrogen and progesterone can cause these growths. They increase the risk of pregnancy loss, and are a contributor to infertility in women.
Adenomysois
A condition in which endometrial tissue exists within and grows into the uterine wall. adenomyosis may cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, severe cramping, pain during intercourse or blood clots that pass during a period.
Poor Egg Quality
Poor egg quality can be a result of a low ovarian reserve. When the egg of poor quality – genetically and otherwise – implantation fails to take place since the quality of embryo is also compromised. Poor egg quality is a leading cause of infertility in females over 35 years of age.
PCOS or PCOD
PCOD or PCOS is a medical condition in which the woman ovaries produce immature or partially mature eggs in large numbers and over the time these become cysts in ovaries. Due to this ovaries become large and secrete large amount of male hormones (androgens) causing infertility, irregular menstrual cycles, hair loss and abnormal weight gain.
MALE FACTOR
Sperm is the male gamete and a compromise in its quality and/or decrease in its quantity is a cause of infertility in men. If the number of sperms is less or their functionality is not optimal, fertilisation cannot take place.
Less in count : Oligospermia (less than or equal to 15 million / ejaculation)
Decreased motility :Asthenospermia (Less than or equal to 40% )
Abnormal morphology :Teratozoospermia (Less than or equal to 4%)
Absence of sperm : Azoospermia (Nil Count)
Genetic diseases
Either or both partners have genetic diseases that may be inherited by their offspring, an IVF cycle can put checks in place to ensure that a genetically robust embryo is implanted.
Unexplained infertility
In certain cases, the exact cause of infertility is not easily ascertained. Such cases can be treated with IVF technique as a deep dive is done into the patients’ health
Sperm is the male gamete and a compromise in its quality and/or decrease in its quantity is a cause of infertility in men. If the number of sperms is less or their functionality is not optimal, fertilisation cannot take place.
Less in count : Oligospermia (less than or equal to 15 million / ejaculation)
Decreased motility :Asthenospermia (Less than or equal to 40% )
Abnormal morphology :Teratozoospermia (Less than or equal to 4%)
Absence of sperm : Azoospermia (Nil Count)
Genetic diseases
Either or both partners have genetic diseases that may be inherited by their offspring, an IVF cycle can put checks in place to ensure that a genetically robust embryo is implanted.
Unexplained infertility
In certain cases, the exact cause of infertility is not easily ascertained. Such cases can be treated with IVF technique as a deep dive is done into the patients’ health
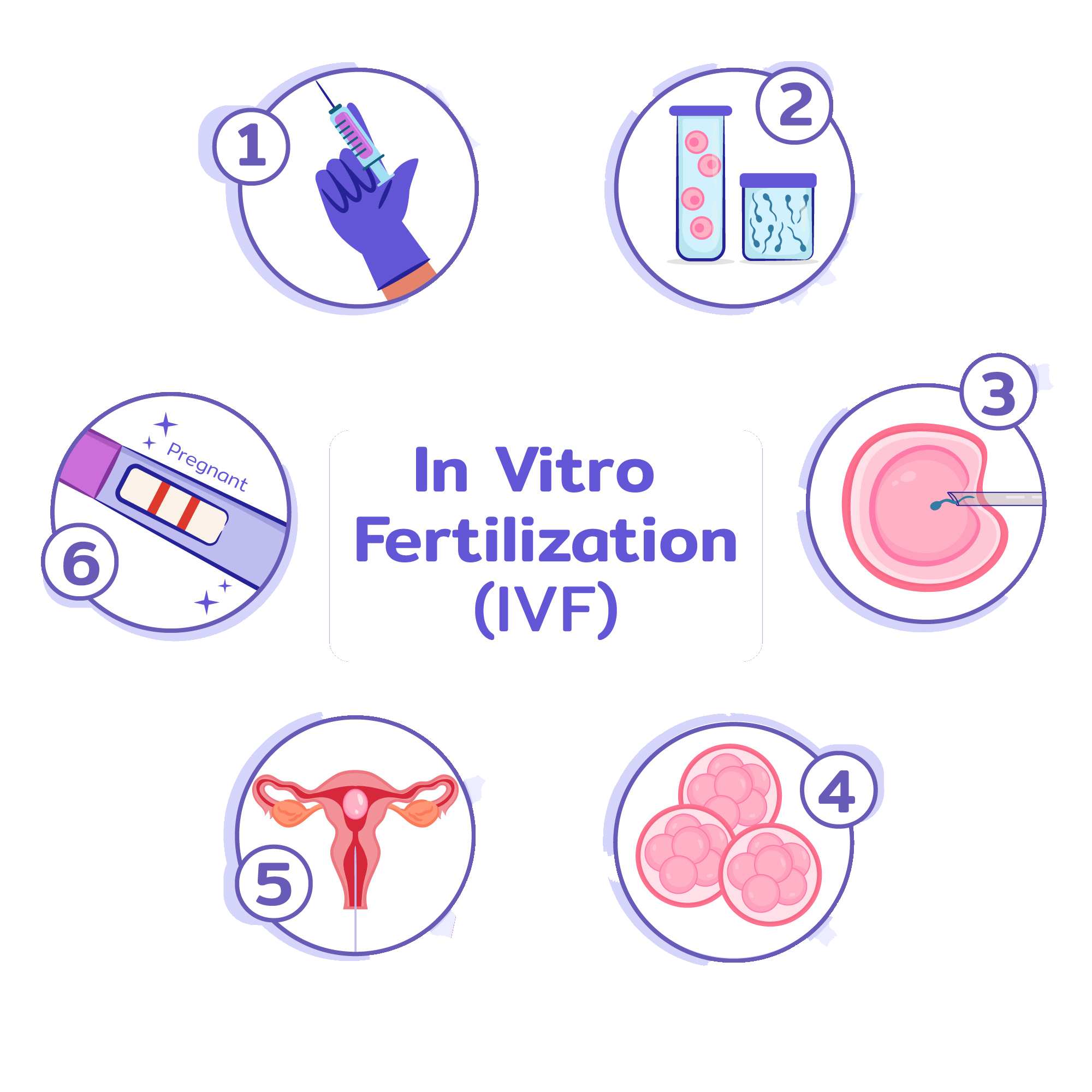
IVF CYCLE OR PROCEDURE
Ovarian Stimulation
Ovarian stimulation occurs with the administration of hormone medications (ovulation drugs) that stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs after a baseline scan (done on day2 or day3 of your cycle).
Monitoring
Regular monitoring is performed through scans and blood tests to observe response to drugs.
Trigger Injection
Once hormone levels (FSH, LH, E2) are at optimal level, a trigger injection is administered to trigger eggs to mature.
Ovum Pickup
Ovum pickup is performed to collect eggs via a needle passed through the vagina; patient is sedated for this procedure. A semen sample collection is done on the day ovum pickup is performed.
Fertilization of Egg
Egg fertilisation takes place by two process IVF AND IVF-ICSI. IVF is used for female infertility and unexplained infertility, and ICSI is used when there is a male cause of infertility.
Embryo formation and Transfer
The best embryos (Day 5 Blastocyst) are transferred into the uterus.
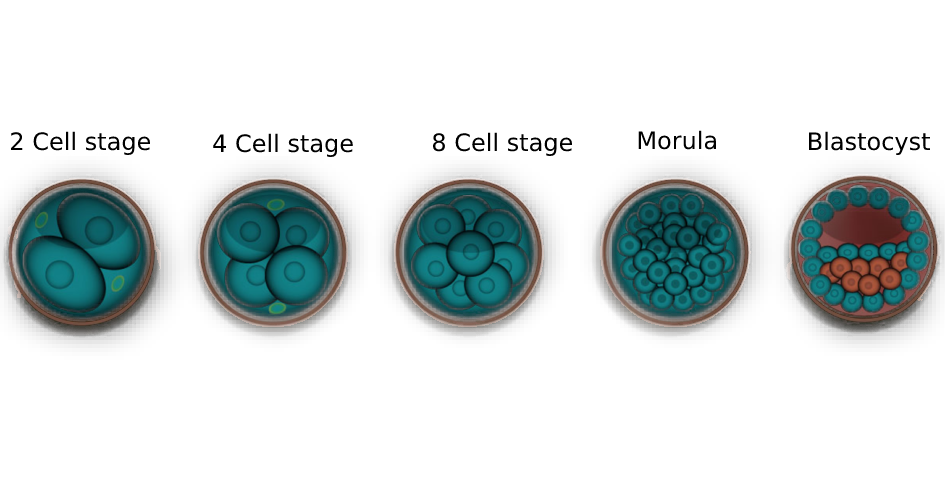
Day 0 - Day of IVF/IVF-ICSI
Day 1 - Fertilization/2 Cell Stage
Day 2 - 4 Cell Stage
Day 3 - 8 Cell stage or more
Day 4 - Morula/Compaction stage
Day 5 - Blastocyst
Do's and Dont's
Do's
1.Prioritise your health. Before you can work towards having a healthy baby, it is essential that you are fit first – both physically and mentally.2.Manage stress and address any challenges you may have by seeking support.
3.Keep yourself physically active by exercising moderately.
4.Sleep 8 hours every night.
5.Keep your nutrition in check – a balanced diet is key and so is keeping track of your vitamins.
6.Give heed to your IVF specialist’s advice.
7.Take it one step at a time and be positive.
Dont's
1.Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking.2.Decrease caffeine intake.
Cost of IVF
IVF cost in India can vary depending on the clinic. In most cases, the IVF treatment cost ranges between INR 1.5 lakh to 2 lakh. The total IVF treatment cost can also depend on any additional surgical procedures that need to be performed.

